Download the valid text in Czech language (link to PDF version of the regulation)
Note: The content of the regulation is identical to the PDF document only in the Czech version. In foreign language versions this is an automatic translation, which is not legally binding.
UH 3
Table of Contents
HLAVA 1. – ÚVODNÍ USTANOVENÍ
HLAVA 2. – TEORETICKÁ PŘÍPRAVA PRO KVALIFIKACI PILOT
HLAVA 3. – PRAKTICKÝ VÝCVIK PRO KVALIFIKACI PILOT
HLAVA 4. – OBSAH VÝCVIKU PRO KVALIFIKACI PILOT
HLAVA 5. – ZKOUŠKA PRO ZÍSKÁNÍ KVALIFIKACE PILOT
HLAVA 6. – PŘEŠKOLOVACÍ VÝCVIK
HLAVA 7. – VÝCVIK PRO KVALIFIKACI INSTRUKTOR
HLAVA 8. – ÚLEVY PŘI VÝCVIKU
HLAVA 9. – VÝCVIK PRO KVALIFIKACI ŘÍZENÉ LETY VFR
HLAVA 10. – VÝCVIK PRO KVALIFIKACI ZKUŠEBNÍ PILOT
HLAVA 11. – PŘÍLOHY
TITLE 1. INTRODUCTORY PROVISIONS
1.1. Tato osnova výcviku pilota ultralehkého vrtulníku (dále jen ULH) stanoví obsah, posloupnost a metodiku přípravy a výcviku na ULH. Je závazná pro všechny žáky, piloty a instruktory, kteří provádějí nebo vedou výcvik pilota ULH.
1.2. Výcvik se provádí na dvoumístných ultralehkých vrtulnících schválených k tomuto účelu inspektorem techniky. Vzhledem k omezeným možnostem ULH může být část výcviku s instruktorem provedena na lehkých vrtulnících normální kategorie, které se hmotností a vlastnostmi příliš neliší od ULH (např. R-22, Schweizer 300).
1.3. ULH, určený pro letecký výcvik ve dvojím obsazení, musí mít úplné dvojí řízení a toto minimální přístrojové vybavení: rychloměr, výškoměr, variometr, příčný sklonoměr, kompas, otáčkoměr motoru, rotoru a palubní intercom.
1.4. ULH musí mít platný technický průkaz vydaný LAA ČR a uzavřeno pojištění odpovědnosti za škody způsobené provozem.
1.5. Meteorologické podmínky při výcviku musí odpovídat podmínkám letu VFR dle UL 1. Pro první samostatný let musí být dohlednost minimálně 2 km.
1.6. Do výcviku může být žák zařazen po dosažení věku 17 let. U osob mladších 18 let se vyžaduje souhlas zákonných zástupců.
1.7. Výcvik je možno provádět ve střediscích pilotního výcviku nebo individuálně instruktorem po odsouhlasení inspektorem provozu. Do osobního listu je nutno vyznačit, ve kterém středisku výcvik proběhl, u individuálních výcviků je nutný písemný souhlas příslušného inspektora provozu v osobním listu před zahájením praktického výcviku.
1.8. Za dodržení postupů výcvikové osnovy odpovídá instruktor provádějící výcvik.
1.9. Odpovědná osoba příslušného střediska pilotního výcviku zodpovídá za dodržení podmínek stanovených předpisem LA 1, výcvikovou osnovou, za provádění údržby SLZ, za splnění závazných
nařízení a za vedení dokumentace střediska pilotního výcviku.
1.10. Výcvik v rámci střediska pilotního výcviku musí být dokumentován v hlavní knize letů střediska pilotního výcviku. V ní musí být uveden každý let s nejméně následujícími náležitostmi: datum letu, typ SLZ, poznávací značka SLZ, jména posádky, doba letu, počet vzletů, cvičení.
1.11. Hlavní kniha letů musí být archivována po dobu činnosti nebo platnosti oprávnění střediska pilotního výcviku.
1.12. Instruktor provádějící výcvik musí mít k dispozici:
1) teaching aids and publications for training,
2) regulations of the LAA of the Czech Republic:
a. LA 1,
b. LA 2,
c. pravidla létání,
d. výcvikovou osnovu,
3) mapu ČR s platnými leteckými informacemi,
4) zákon č. 49/1997 Sb. a vyhlášku č. 108/1997 Sb. v potřebném rozsahu a platném znění.
1.13. Během praktického výcviku musí mít k dispozici:
1) prostředky pro poskytnutí první pomoci,
2) pojítko pro spojení se střediskem rychlé zdravotní pomoci,
3) hasící prostředky,
4) ukazatel směru a síly větru.
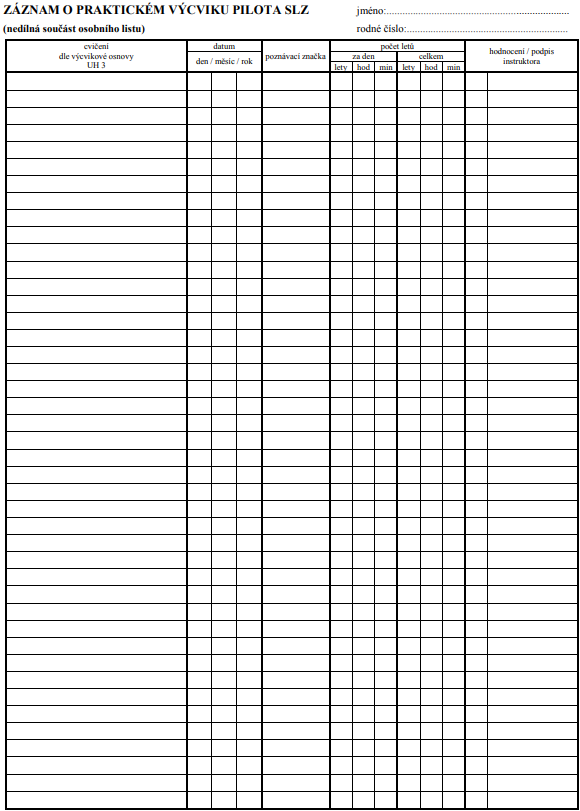
1.14. Instruktor vede dokumentaci výcviku formou osobních listů v průběhu výcviku a po jeho skončení formou kopií osobních listů.
1.15. Výcvik s výjimkou nácviku přistání v terénu je nutno provádět pouze z letiště, heliportu, či plochy pro SLZ.
1.16. Praktickou část výcviku pilota ULH lze zahájit až po absolvování nejméně 50 % rozsahu teoretické výuky. Celý rozsah teoretické výuky musí být probrán nejpozději před samostatným navigačním letem.
1.17. Před zahájením praktického výcviku musí být žák seznámen s ULH minimálně v tomto rozsahu:
1) technický popis,
2) letová příručka,
3) obsluha a údržba,
4) předletová prohlídka,
5) palubní nácvik,
6) důležité úkony,
7) nouzové postupy.
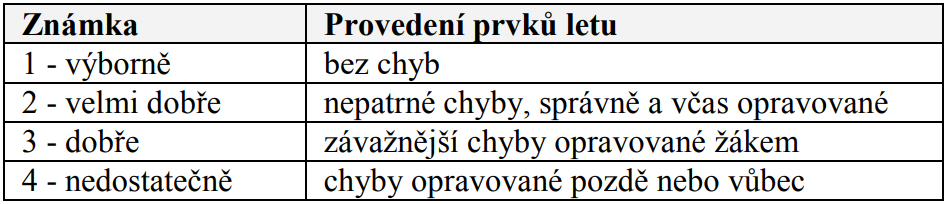
1.18. Při hodnocení žáků v praktické části výcviku jsou instruktoři povinni používat této známkovací stupnice:
1.19. Počty letů a hodin v osnově jsou minimální. O skutečném počtu letů rozhodne instruktor na základě zvládnutí požadovaných návyků a dovedností žákem.
1.20. Instruktor povoluje postup žáka na další cvičení dle osnovy pouze tehdy, pokud je žák hodnocen známkou 1 nebo 2. Je-li hodnocen známkou 3 zůstává na daném cvičení, při hodnocení známkou 4 se vrací na předchozí cvičení.
1.21. Před každým praktickým cvičením osnovy obsahujícím nové prvky, provádí instruktor se žákem pozemní přípravu v takovém rozsahu, aby bylo zajištěno dokonalé pochopení cvičení žákem.
1.22. Žák může nalétat během jednoho letového dne max. 4 hodiny.
1.23. První samostatný let žáka povoluje instruktor, který vedl výcvik a má komplexní přehled o žákovi. Přezkoušení před samostatným letem je nutné plánovat tak, aby žák mohl v tentýž den provést ještě nejméně jeden samostatný let. Pokud se samostatný let týž den z jakýchkoli důvodů neuskuteční, je třeba provést nové přezkoušení. V den prvního samostatného letu smí žák vykonat maximálně 3 samostatné lety.
1.24. Na praktickém výcviku žáka se mohou podílet maximálně 2 instruktoři.
1.25. Žák nesmí provádět samostatné lety bez dozoru instruktora.
1.26. Žák se souběžně nesmí účastnit více druhů leteckého výcviku.
1.27. Závěrečnou zkoušku provádí inspektor provozu.
1.28. Pro vydání průkazu pilota ULH se uznává letová doba a ekvivalentní cvičení odlétaná s instruktorem na vrtulníku normální kategorie blížící se svojí hmotností a vlastnostmi ULH (např. Schweizer-300 nebo R-22) v registrovaném zařízení pro výcvik PPL(H), nebo v FTO. Všechna cvičení splněná na vrtulníku normální kategorie se procvičí na ULH v rozsahu, který určí instruktor. Je vhodné, nikoli však nutné, aby instruktorem na vrtulníku normální kategorie i ULH byla jedna osoba.
1.29. Rotor ULH je povoleno uvádět motorem do pohybu jen, je-li v kabině za řízením instruktor, pilot nebo žák oprávněný k samostatným letům. Tento smí vystoupit až po úplném zastavení rotoru.
TITLE 2. THEORETICAL TRAINING FOR THE PILOT RATING
2.1. Teoretická příprava je první částí výcviku pilota ULH. Je prováděna instruktorem nebo lektory s odpovídajícími znalostmi daného předmětu. Účast na této přípravě je hodnocena a evidována instruktorem vedoucím výcvik. Posloupnost teoretické přípravy musí být taková, aby bylo vždy zajištěno správné pochopení látky daného předmětu v dostatečném předstihu před praktickou částí výcviku.
2.2. Vyučovací předměty a rozsah výuky

2.3. Okruhy požadovaných znalostí:
2.3.1. Aerodynamika:
1) Základní fyzikální pojmy a měrové jednotky.
2) Aerodynamický odpor, závislost odporu na rychlosti.
3) Proudnice, třecí odpor, mezní vrstva, víry.
4) Vzorec aerodynamického odporu, činitelé jej ovlivňující, Bernoulliho rovnice.
5) Rovnice kontinuity, praktický význam a využití
6) Vztlak a odpor ploché desky.
7) Obtékání a tlaky kolem profilu, tětiva, úhel náběhu, rozložení tlaku, výslednice tlaku.
8) Celková reakce profilu křídla v proudu vzduchu, změna polohy, výslednice tlaku (neustálené a ustálené proudění).
9) Vztlak a odpor profilu, součinitel vztlaku, součinitel odporu, kritický úhel náběhu.
10) Ideální profil (aerodynamické a geometrické charakteristiky), indukovaný odpor, interference.
11) Metody vyvolání tahu, vrtule, tryskový pohon.
12) Vodorovný let, rozhodující síly, rovnováha si, ocasní plochy a jejich zatížení.
13) Vodorovný let při různých rychlostech, vztah mezi rychlostí a úhlem náběhu.
14) Vliv výšky a hmotnosti na rychlost a úhel náběhu.
15) Základní pojmy aerodynamiky vrtulníků.
16) Nosný rotor, jeho funkce, popis obtékání a aerodynamických jevů v jednotlivých režimech letu.
17) Prostředky pro kompenzaci reakčního momentu a směrového řízení (ocasní vrtulka, fenestron, NOTAR).
18) Lety v režimu autorotace.
19) Nebezpečné jevy vznikající při provozu UL vrtulníku (vírový prstenec rotoru či ocasní vrtulky, nízké a vysoké otáčky rotoru, podchvat, nízké „G“, pozemní rezonance, graf nebezpečných oblastí).
2.3.2. Stavba a konstrukce SLZ:
1) Definice letadlo, letoun, vrtulník, SLZ, rozdělení letadel.
2) Názvosloví, popis SLZ.
3) Materiály použité při konstrukci SLZ.
4) Únava a opotřebení materiálu.Rezursy.
5) Druhy konstrukcí, jejich vlastnosti.
6) Zatížení konstrukce, součinitel bezpečnosti, násobek.
7) Konstrukce ULH.
8) Rotorové hlavy, druhy a konstrukce, vlastnosti.
9) Řízení ULH.
10) Podvozky, tlumiče, řízení, palivový, olejový a elektrický systém draku.
11) Předpisy pro stavbu a provoz ULH, PLZ a ostatní dokumenty.
2.3.3. Předpisy:
1) Pravidla vyhýbání a zabraňování srážkám.
2) Výklad pojmů CTR, TMA, ATZ a lety v těchto prostorech
3) Druhy vytýčení na návěštní ploše letiště a na VPD
4) Provoz ULL dle předpisů LA, L2, L6.
5) Práce s AIP, NOTAM, Letecký oběžník, základní zkratky.
6) Podmínky pro získání a prodloužení platnosti průkazu pilota ULH.
7) Druhy kvalifikací pro létání s ULH a jejich získávání.
8) Meteorologické limity pro lety s ULH.
9) Podmínky pro provedení letu VFR dle UL1.
10) Podmínky pro přílet ULH na letiště AFIS.
11) Předletová prohlídky ULH.
12) Výběr trasy letu, oblet a přelétávání překážek.
13) Samostatný provoz ULH, parametry plochy a překážkové roviny.
14) Klasifikace vzdušného prostoru ČR.
15) Kontrola provozu, právo odebírání průkazu pilota ULH.
16) Postupy pro nastavení výškoměru. Vyjadřování výšky.
17) Podmínky a způsob použití radiostanic v letovém provozu ULH.
18) Dohlednost, letová dohlednost.
19) Společný provoz ULH a letadel na letišti AFIS.
20) Odpovědnost za dodržení podmínek pro lety ULH.
21) Získávání informací pro bezpečné provedení letu.
22) Druhy letišť v ČR.
23) Výklad pojmů LKP, LKR, TRA, TSA jejich aktivace, možnost letů do nich.
24) Podmínky pro přistání ULH mimo letiště, schválené heliporty a plochy pro SLZ.
2.3.4. Navigace
1) Tvar a rozměry zeměkoule, rovnoběžky a poledníky.
2) Zeměpisná šířka a délka, druhy navigace při létání.
3) Časová pásma.
4) Velká a malá kružnice na zeměkouli.
5) Mapy, měřítka, druhy zobrazení topografické situace.
6) Loxodroma a ortodroma.
7) Východ a západ slunce – posun v ročních obdobích.
8) Srovnávací navigace.
9) Navigační příprava, výpočty, vliv větru.
10) Kompas, princip, použití, deviace, deklinace.
11) Isogony.
12) Řešení vektorového trojúhelníku.
13) Postupy při ztrátě orientace.
14) Akční rádius, jeho definování a zjištění.
2.3.5. Meteorologie:
1) Zemská atmosféra, složení a tlak vzduchu.
2) Teplota, tlak a vlhkost vzduchu.
3) Tlakové útvary, cirkulace vzduchové hmoty.
4) Studená a teplá fronta, okluze.
5) Vítr, vznik, rychlost, směr, měření, turbulence.
6) Vznik bouřek, nebezpečí pro létání.
7) Rody oblačností a druhy oblaků.
8) Veličiny měřené při meteorologickém výstupu, graf.
9) Nasycená a nenasycená vzduchová hmota, rosný bod.
10) Význam znalosti meteorologie pro létání.
11) Podmínky pro tvořen námrazy, kritická místa.
12) Určování dohlednosti, jevy ovlivňující dohlednost.
13) Základní meteorologické zkratky a kódy.
14) Zdroje meteo informací, zprávy, předpovědi a výstrahy.
15) Nebezpečné povětrnostní jevy.
2.3.6. Motory, přístroje:
1) Popis činnosti dvoudobého motoru, jeho části.
2) Popis činnosti čtyřdobého motoru, jeho části.
3) Složení a příprava směsi nasávané do válců.
4) Způsoby mazání dvoudobého a čtyřdobého motoru.
5) Karburátor – princip, výhody a nevýhody.
6) Vstřikování paliva – princip, výhody a nevýhody.
7) Druhy zapalování zážehových motorů.
8) Výkony, spolehlivost a životnost motorů používaných v ULH.
9) Charakteristické poruchy motorů ULH a jejich příčiny.
10) Význam prohřátí motoru před letem, motorová zkouška.
11) Vliv námrazy na výkon, předcházení a odstraňování. Námraza v karburátoru.
12) Náběhová a volnoběžná spojka, účel a konstrukce.
13) Statický, celkový a dynamický tlak.
14) Magnetický kompas s přímým čtením, princip, použití.
15) Zatáčkoměr a příčný sklonoměr.
16) Rychloměr.
17) Barometrický výškoměr, nastavení.
18) Variometr.
19) Otáčkoměry.
20) Teploměry oleje, hlav válců, vnějšího vzduchu.
2.3.7. Spojovací předpis:
1) Radiotelefonní spojení, hlas, řeč, hláskovací abeceda, vysílání čísel.
2) Slova a fráze.
3) Udávání času.
4) Navázání a ukončení radiového spojení.
5) Zkušební vysílání, stupnice čitelnosti.
6) Vysílání naslepo, přednostní pořadí.
7) Volací značky leteckých stanic a letadel.
8) Zkrácené volací značky letadel, opravy a opakování.
9) Nouzové postupy, kmitočty, tísňový a pilnostní provoz.
10) Činnost letadla v tísni, činnost ostatních letadel.
11) Uložení ticha, zrušení tísně.
12) Korespondence se službou AFIS
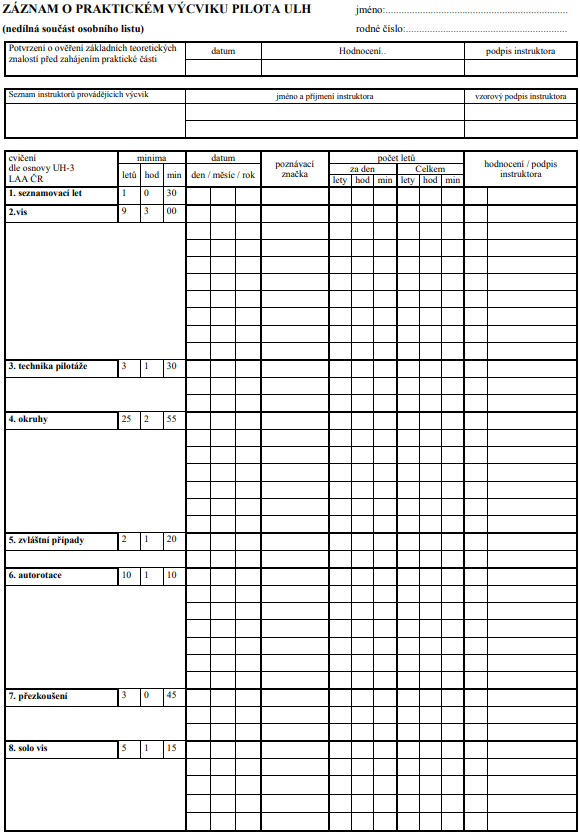
HLAVA 3. PRAKTICKÝ VÝCVIK PRO KVALIFIKACI PILOT
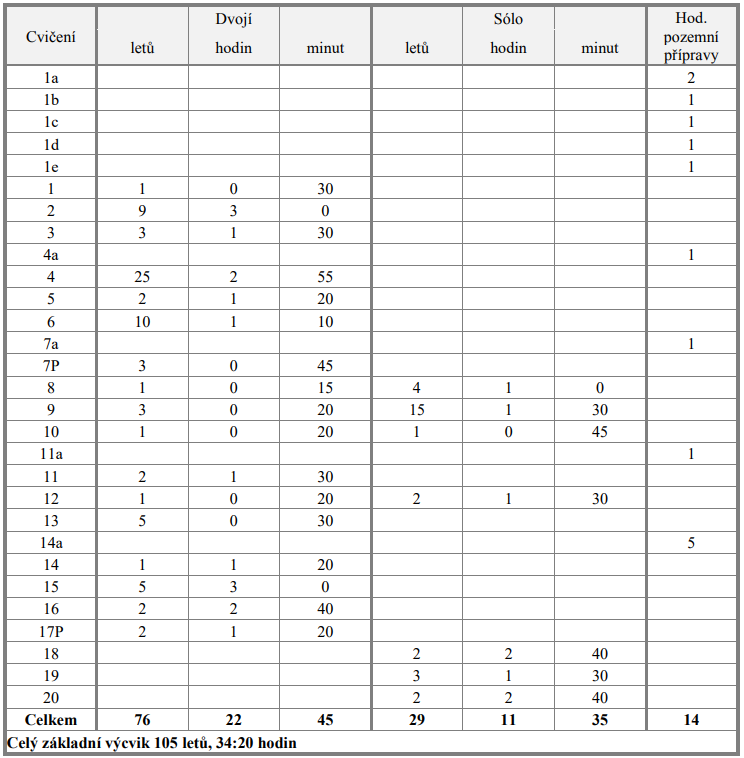
HLAVA 4. OBSAH VÝCVIKU PRO KVALIFIKACI PILOT
4.1. Cvičení 1a (Pozemní příprava)
Seznámení s letovou příručkou ULH:
1) základní technické údaje
2) rozmístění ovladačů, přístrojů, radiostanic a jejich používání
3) způsob plnění LPH a olejů, bezpečnostní předpisy
4) normální a nouzové postupy
5) provozní omezení
6) výkony, hmotnosti, centráže
4.2. Cvičení 1b (Pozemní příprava)
Předletová prohlídka, spouštění a zahřívání motoru, motorová zkouška a vypnutí:
1) provedení předletové prohlídky
2) nastupování do ULH a vystupování
3) úkony před spouštěním
4) postup spouštění a zahřívání
5) motorová zkouška
6) chlazení a vypnutí motoru
7) prohlídky po letu
4.3. Cvičení 1c (Pozemní příprava)
Účinky řízení, vyvážení, ovládání motoru:
popis a vysvětlení reakcí vrtulníku na pohyby řízením, popis manipulace s řízením a ovládáním motoru při jednotlivých manévrech (ve visu a za letu)
4.4. Cvičení 1d (Pozemní příprava)
Seznámení se způsobem provedení vzletu (odpoutání) a letu ve visu:
1) rozdělení pozornosti
2) zásahy do řízení
3) způsob kontroly přístrojů
4) poloha horizontu na kabině za letu
5) chyby a jejich opravy
4.5. Cvičení 1e (Pozemní příprava)
Seznámení s organizací, řízením a zabezpečením letového provozu
1) služby při provozu
2) radiokorespondence
3) seznámení s letištěm a jeho prostory
4) překážky a orientační body
4.6. Cvičení 1. Seznamovací let
výška letu: 1 – 1500 ft (0,3 – 500 m) AGL
Předvedení pilotáže při vzdušném pojíždění, visení, vzletu, stoupání. V prostoru zatáčky o různých náklonech, manévry rychlostí, klesání s výkonem motoru i autorotací, seznámení s prostorem letiště i pracovními prostory, zařazení do okruhu, rozpočet na přistání, přistání. Let provádí instruktor, žák drží lehce řízení, orientuje se v prostoru a sleduje radiokorespondenci.
Podmínky splnění: absolvování letu.
4.7. Cvičení 2. Cvičné lety na režimu visení
výška letu: 1 – 10 ft (0,3 – 3 m) AGL
Nácvik visení na místě (v oblasti příz. efektu), svislé odpoutání a dosednutí, otáčení ve visu na místě, posuny do stran, dopředu a dozadu.
Zaměřit se na plynulost provádění prvků bez zbytečných a prudkých zásahů do řízení, dodržování stálé výšky. Postupně dosáhnout schopnosti pohybu po obvodě vytyčeného čtverce (30 x 30 m) a dosednutí na cíl.
Podmínky splnění: Odpoutat vrtulník od země bez nepřiměřených náklonů, pootočení a posuvů, udržet vrtulník v klidu ve visu, provést pohyb po obvodě čtverce ve stanovené výšce, otočky na obě strany a dosednutí na cíl.
4.8. Cvičení 3. Cvičné lety v prostoru k nácviku základních prvků pilotáže
výška letu: 500 – 1500 ft (150 – 500 m) AGL
Nácvik přímého horizontálního letu cestovní rychlostí, zatáčky o náklonech 15 a 30 stupňů, stoupání a klesání o různých klesacích a dopředných rychlostech v přímém směru i v zatáčkách. Manévr rychlostí od minimální po maximální s dodržením výšky a směru.
Odlet do prostoru, zařazení do okruhu a přistání provádí instruktor.
Podmínky splnění: Zvládnout s přiměřenou přesností výše uvedené prvky jednoduché pilotáže
4.9. Cvičení 4a. (Pozemní příprava)
Pozemní příprava k letům po okruhu a řešení zvláštních případů za letu.
1) seznámení se způsobem provedení vzletu, letu po okruhu a s rozpočtem na přistání
2) pilotáž při mezních rychlostech
3) způsob přechodu do autorotace a pilotáž v autorotaci
4) způsob pilotáže při vzletu s minimálním potřebným výkonem
4.10. Cvičení 4. Cvičné lety po okruhu
výška letu: 1000 a 500 ft (300 a 150 m) AGL
Nácvik vzletu, letu po kruhu, rozpočtu a přistání. Po odpoutání do visu ve výšce 2 – 6 ft (0,6 – 2 m) nacvičit plynulý přechod dopředného letu a stoupání, provedení pravidelného okruhu s vylučováním snosu, zastavení ve visu ve výšce 2 – 6 ft (0,6 – 2 m) a dosednout. První a čtvrtou zatáčku v minimální výšce 300 ft (100 m), v první zatáčce náklon max. 15 stupňů, ostatní zatáčky maximálně 30 stupňů.
Podmínky splnění: Provést let po okruhu, s přiměřenou přesností dodržet rychlost, výšku letu, tvar okruhu, stanovený režim motoru a přistát správným rozpočtem na určeném místě.
4.11. Cvičení 5. Lety v prostoru k řešení zvláštních případů za letu
výška letu: 500 – 1500 ft (150 – 500 m) AGL
Lety na mezních rychlostech, lety na režimu autorotace, nouzové postupy, opuštění vírového prstence, obnovení nízkých otáček rotoru.
Vzlet, odlet do prostoru a zařazení do okruhu provádí žák.
Podmínky splnění: Včas a správnými postupy reagovat na simulované zvláštní případy za letu.
4.12. Cvičení 6. Vzlety a přistání s minimálním potřebným výkonem, rozpočty autorotací
výška letu: 500 – 1000 ft (150 – 300 m) AGL
U vrtulníku s kolovým podvozkem nacvičit vzlet a přistání s rozjezdem a dojezdem, u ostatních vzlet a přistání s využitím vzduchového polštáře. Rozpočty na přistání autorotací (do visu) v přímém směru a zatáčkou.
Podmínky splnění: Provést vzlet a přistání s minimálním potřebným výkonem, provést autorotační sestup s dodržením stanovené rychlosti a otáček nosného rotoru do visu.
4.13. Cvičení 7a (Pozemní příprava)
Pozemní příprava před přezkoušením na samostatné lety
1) zopakování nouzových postupů
2) seznámení s provedením samostatného letu
3) odlišnosti v pilotáži při sólovém obsazení
4.14. Cvičení 7P Přezkoušení před samostatnými lety
výška letu: do 1500 ft (do 500 m) AGL
Přezkoušení z techniky pilotáže ve visu, při letu po okruhu a v prostoru. Ve visu přezkoušet všechny prvky z cvičení 2., při letu po okruhu přezkoušet správnost provedení okruhu ve výšce 1000 a 500ft (300 a 150 m), rozpočet na přistání a dosednutí z visu, v prostoru přezkoušet stoupání v přímém směru i v zatáčkách, zatáčky v horizontálním letu s náklony 15 a 30 stupňů, minimální a maximální rychlost s dodržením přímého směru a výšky, klesání s výkonem v přímém směru i v zatáčkách, klesání v autorotaci, nouzové postupy a zařazení do okruhu a přistání.
Podmínky splnění: Provést všechny výše uvedené prvky v takové přesnosti a kvalitě, aby nevznikla pochybnost o zvládnutí samostatného letu.
4.15. Cvičení 8. Samostatné a kontrolní lety ve visu.
výška letu: 1 – 10 ft (0,3 – 3 m) AGL
Svislé vzlety a přistání, ve visu otáčení a posuny do stran, dozadu a dopředu s dodržením výšky a určeného prostoru, vyloučit neklidné pohyby řízením a vrtulníkem.Dle uvážení instruktora provést v průběhu plnění cvičení kontrolní lety.
Podmínky splnění: hodnocení 1-2.
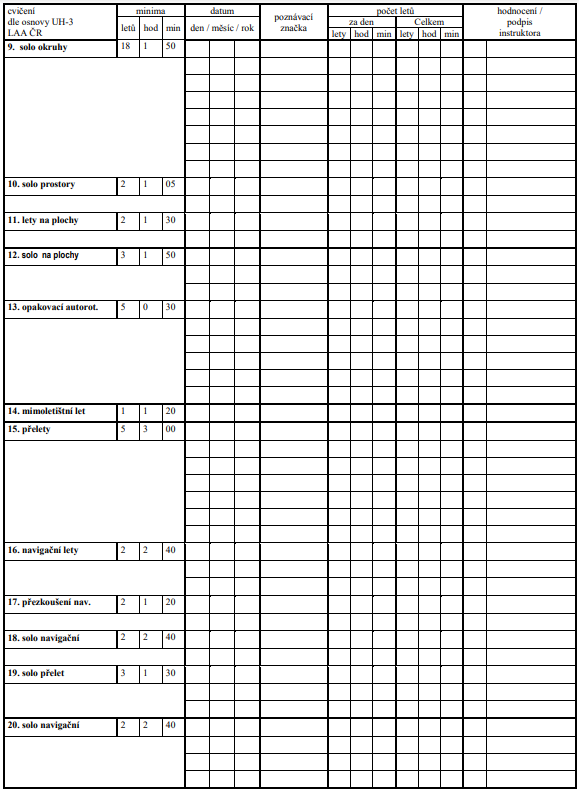
4.16. Cvičení 9. Samostatné a kontrolní lety po okruhu
výška letu: 1000 a 500 ft (300 – 150 m) AGL
Vzlet a přistání z visu, první a čtvrtá zatáčka minimálně ve 300 ft(100 m), náklon v 1. zatáčce max. 15 stupňů, v ostatních max. 30 stupňů. Nezdařené přiblížení nesmí být opravováno intenzivním brzděním – “natažením” vrtulníku, ale opakováním okruhu. Přechod do visu ve výšce 2 – 6 ft (0,6 – 2 m). Dle uvážení instruktora provést před plněním cvičení, nebo v jeho průběhu kontrolní lety.
Podmínky splnění: hodnocení 1-2.
4.17. Cvičení 10. Samostatné a kontrolní lety v prostoru
výška letu: 500 – 1500 ft (150 – 500 m) AGL
Po kontrolním letu s instruktorem provést samostatné lety do prostoru k cvičení stoupání a klesání v přímém směru i v zatáčkách, zatáčky s náklonem 15 a 30 stupňů s dodržením směru, zařazení do okruhu a rozpočet na přistání.
Podmínky splnění: hodnocení 1-2.
4.18. Cvičení 11a. (pozemní příprava)
Pozemní příprava pro lety na plochy omezených rozměrů.
seznámení žáka s metodikou letu a s technikou pilotáže
4.19. Cvičení 11. Cvičné lety na plochy omezených rozměrů
výška letu: 500 ft (150 m) AGL
Pro nácvik zvolit v terénu plochu o rozměrech 100 x 100 m, zjistit směr větru a zvolit směr přiblížení, provést průlet k prohlídce plochy ve výšce min. 60 ft (20 m) nad překážkami v horizontálním letu rychlostí min. 30 kt (55 km/h), provést okruh ve výšce 500 ft (150 m) a rozpočet do visu nad místem přistání s minimální výškou nad překážkami 30 ft (10 m) při přiblížení, sestup a dosednutí v místě s vyhovujícím sklonem plochy. Vzlet a stoupání minimálně 30 ft (10 m) nad překážky ve směru vzletu, rozlet a přechod do stoupání.
Upozornit na možnost závětří za překážkami a případný sklon či nerovnosti plochy v terénu a vysvětlit řešení v takových situacích.Plocha musí splňovat podmínky stanovené v let.zákoně a ostatních předpisech.
Podmínky splnění: Prokázat schopnost vybrat v terénu vhodnou plochu pro přistání, při průletu ověřit její způsobilost k přistání, provést okruh a správný rozpočet.
4.20. Cvičení 12. Samostatné a kontrolní lety na plochy omezených rozměrů.
výška letu: 500 ft (150 m) AGL
Samostatně v rozsahu cv. 11. Dle uvážení instruktora provést před provedením cvičení, nebo v jeho průběhu kontrolní let.
Podmínky splnění: hodnocení 1-2.
4.21. Cvičení 13. Pokročilé autorotace
výška letu: 500 – 1000 ft (150 – 300 m) AGL
Provést vzlety s minimálním potřebným výkonem, rozpočet na přistání autorotací s náročnějšími manévry.
Podmínky splnění: Zvládnout autorotační sestupy a rozpočty se složitějšími manévry (zatáčkou o 180 °, zkrácení rozpočtu manévrem ve tvaru písmene „S“).
4.22. Cvičení 14a. (pozemní příprava)
Pozemní příprava k provádění navigačních letů.
1) příprava mapy
2) navigační štítek, výpočty, vyplňování
3) způsob naletění a udržování kurzu na trati
4) činnost při ztrátě orientace
5) činnosti při zhoršení povětrnostních podmínek
6) činnost při zvláštních případech za letu
7) radiové spojení
8) postupy při letu na cizí letiště
9) zjišťování omezení ve vzdušném prostoru a dalších potřebných informací
10) zjišťování stavu a předpovědi počasí
4.23. Cvičení 14. Navigační let
výška letu: 700 – 1000ft (200 – 300 m) AGL
Navigační let v délce min. 120 km alespoň přes čtyři otočné body.
Podmínka splnění: Vedení vrtulníku po stanovené trase s přiměřenou přesností, vedení navigačního záznamu.
4.24. Cvičení 15. Přelety
výška letu: 700 – 1000 ft (200 – 300 m) AGL
Nácvik navigace při letech, alespoň jeden let v celkové délce 150 km, během výcviku s přistáním min. na 3 cizích letištích či plochách SLZ
Podmínka splnění: Vedení vrtulníku po stanovené trase s přiměřenou přesností, vedení navigačního záznamu. Správný postup příletu na cizí letiště či plochu pro SLZ včetně přistání, vzletu a odletu.
4.25. Cvičení 16. Navigační lety ve výšce 500 ft (150 m) AGL
výška letu: 500 ft (150 m) AGL
Lety v délce min. 120 km.
Podmínka splnění: Vedení vrtulníku po stanovené trase v 500 ft (150 m) AGL s přiměřenou přesností, vedení navigačního záznamu.
4.26. Cvičení 17P. Přezkoušení z navigačního vedení letadla po trati
ve dvojím: 2 lety, 1 hod 20 min
výška letu: 500 – 1000 ft (150 – 300 m) AGL
Trať minimálně 120 km dlouhá, s přistáním na letišti či ploše SLZ, na které žák při výcviku nepřistával.
Podmínka splnění: Vedení vrtulníku po stanovené trase s přiměřenou přesností, vedení navigačního záznamu. Správný postup příletu na cizí letiště či plochu pro SLZ včetně přistání, vzletu a odletu.
4.27. Cvičení 18. Samostatný navigační let
výška letu: 700 – 1000 ft (200 – 300 m) AGL
Mimoletištní let po trati min. 120 km dlouhé se 3 otočnými body. Letěnou trať volit v prostoru, v kterém byla provedena cvičení 14a až 17P.
Podmínky splnění: hodnocení 1-2.
4.28. Cvičení 19. Samostatný přelet
výška letu: 700 – 1000ft (200 – 300 m) AGL
Přelet po trojúhelníkové trati o celkové délce min. 150 km s přistáním na dvou letištích či plochách pro SLZ. Doporučuje se, aby v místě přistání byla poučená osoba.
Podmínky splnění: hodnocení 1-2.
4.29. Cvičení 20. Samostatné navigační lety ve výšce 500 ft (150 m) AGL
výška letu: 500 ft (150 m) AGL
Mimoletištní lety v délce min.120 km s nejméně 4 otočnými body.
Podmínky splnění: hodnocení 1-2.
HLAVA 5. ZKOUŠKA PRO ZÍSKÁNÍ KVALIFIKACE PILOT
5.1. Praktickou zkoušku lze provést po úspěšném ukončení teoretického i praktického výcviku a teoretické zkoušky. Teoretickou část zkoušky lze provést kdykoliv v průběhu výcviku nejdříve však po prvním samostatném letu. Platnost teoretické zkoušky je 90 dní. Po uplynutí platnosti je třeba teoretickou zkoušku opakovat. Praktickou zkoušku provádí inspektor provozu, který se nepodílel na výcviku žáka více než 50%.
5.1.1. Teorie
schváleným zkušebním testem. Není-li k dispozici aktuálně schválený test pro piloty ULH, využije se test určený pro piloty ULL a inspektor písemně či ústně ověří znalosti týkající se ULH. Výsledek teoretické zkoušky potvrdí inspektor provozu do osobního listu. Teoretická část předchází praktické. V případě neúspěchu je možné ji opakovat nejdříve po 14 dnech.
5.1.2. Praxe:
praktická část zkoušky se provádí po úspěšném složení teoretické části zkoušky potvrzené v osobním listě žáka v době platnosti teoretické zkoušky. Praktická zkouška musí obsahovat minimálně 4 lety ve dvojím v minimální době trvání 40 min. Provádí se ve čtverci pro visení, na okruhu a v prostoru. Přezkouší se všechny prvky jako ve cvičení 7P a 11.
5.1.3. Teoretickou i praktickou část zkoušky lze opakovat maximálně 4x. V případě vyčerpání maximálního počtu pokusů bude žadateli stanoven potřebný rozsah doplňujícího výcviku.
5.1.4. Podmínka splnění:
Hodnocení 1 až 3 v praktické části zkoušky, v teoretické části dosažený předepsaný počet bodů.
Výsledek zkoušky zaznamenává inspektor do osobního listu žáka.
HLAVA 6. PŘEŠKOLOVACÍ VÝCVIK
6.1. Přeškolení na ULH případně na další typ ULH provádí pilot s kvalifikací instruktora ULH.
6.2. Přeškolení dle této osnovy je možno provést:
1) Pilotům s platným průkazem pilota ULH – (přeškolení na další typ ULH)
2) Soukromým pilotům vrtulníků – (za účelem získání průkazu pilota ULH)
3) Obchodním pilotům vrtulníků – (za účelem získání průkazu pilota ULH)
4) Dopravním pilotům vrtulníků – (za účelem získání průkazu pilota ULH)
5) Pilotům vojenských vrtulníků – (za účelem získání průkazu pilota ULH)
6.3. O schopnosti pilota provést samostatný let na dvoumístném ULH rozhoduje instruktor, který provádí přeškolení. Podmínkou přeškolení na jednomístný ULH je platný průkaz pilota ULH a celkový nálet na ULH minimálně 50 letových hodin, z toho samostatně nejméně 20 letových hodin. V tomto případě provede instruktor oprávněný létat dané typy s přeškolovaným kontrolní let na dvoumístném ULH v rozsahu cv.28 se zaměřením na simulaci vlastností jednomístného ULH a posoudí jeho schopnost pilotovat jednomístný ULH. Po provedení příprav provede přeškolovaný veškeré lety (včetně cv.22,23 a 24) samostatně. Cvičení 28 se již znovu na jednomístném ULH neprovádí.
6.4. Má-li přeškolovaný platný průkaz pilota ULH, provádí přezkoušení dle cv.28 instruktor a přeškolovaný tím získá oprávnění létat další typ ULH. U zalétávacích (zkušebních) pilotů se přeškolení nevyžaduje.
6.5. U pilotů uvedených v bodech 2, 3, 4, 5, kteří hodlají získat průkaz pilota ULH provádí pilotní zkoušku dle cv. 28 inspektor.
6.6. Teoretická příprava:
Uchazeči uvedení v úvodním ustanovení body 2), 3), 4), 5) absolvují přezkoušení z předpisů LAA a z předmětu STAVBA KONSTRUKCE SLZ.
6.7. Osnova praktické části přeškolovacího výcviku pilota ULH.
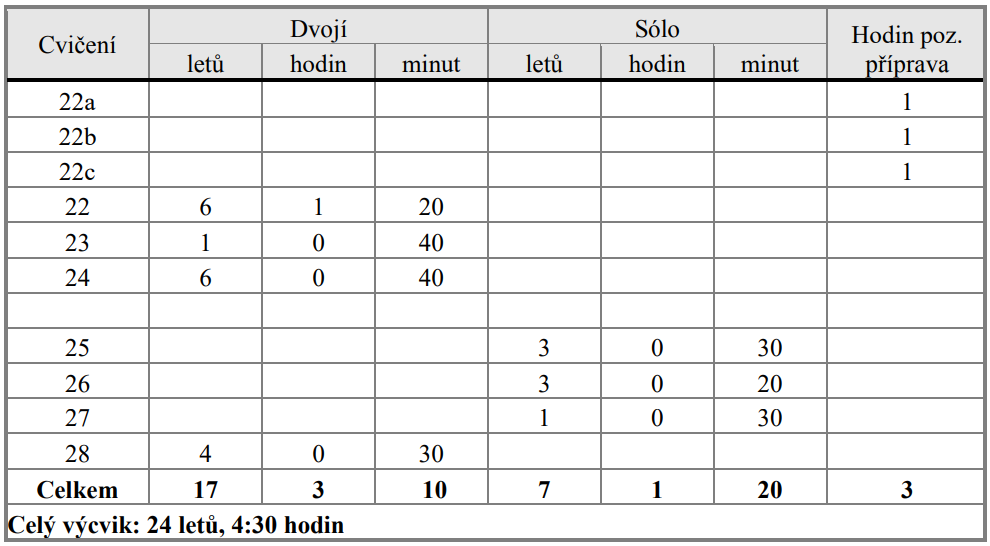
6.8. Cvičení 22a (Pozemní příprava)
Seznámení s letovou příručkou ULH:
1) základní technické údaje
2) rozmístění ovladačů, přístrojů, radiostanic
3) způsob plnění LPH a olejů
4) normální a nouzové postupy
5) provozní omezení
6) výkony, hmotnosti, centráž
6.9. Cvičení 22b (Pozemní příprava)
Předletová prohlídka, spouštění, zahřívání motoru, motorová zkouška, vypnutí
1) provedení předletové prohlídky
2) nastupování do ULH a vystupování
3) úkony před spouštěním
4) postup spouštění a zahřívání
5) motorová zkouška
6) chlazení a vypnutí motoru
7) prohlídka po letu
6.10. Cvičení 22c (Pozemní příprava)
Studium a přezkoušení z postupů UL-1 a LA-1:
Toto cvičení není povinné pro piloty uvedené v ustanovení 6.2. odst. 1)
6.11. Cvičení 22 Cvičné lety na režimu visení
výška letu: 1-10 ft (0,3 – 3 m) AGL
Nácvik visení na místě, svislé odpoutání a dosednutí, otáčení ve visu na místě, posuny do stran, dopředu a dozadu. Provádí se ve čtverci 30 x 30 m.
Podmínky splnění: Odpoutat vrtulník od země bez nepřiměřených náklonů, pootočení a posuvů, udržet vrtulník v klidu ve visu, provést pohyb po obvodě čtverce ve stanovené výšce, otočky na obě strany a dosednutí na cíl.
6.12. Cvičení 23. Cvičné lety v prostoru
výška letu: do 1500 ft (500 m) AGL
Seznámení s letovými vlastnostmi ULH a s obsluhou veškerého vybavení používaného za letu. Let v rozsahu povolených rychlostí od minimální do maximální. Zatáčky o náklonu 15 a 30 stupňů v horizontálním letu, ve stoupání a klesání. Řešení zvláštních případů za letu, klesání autorotací v přímém směru i zatáčkách do visení. Přistání na plochu omezených rozměrů.
Podmínky splnění: Zvládnout s přiměřenou přesností výše uvedené prvky jednoduché pilotáže.
6.13. Cvičení 24. Cvičné lety po okruhu
výška letu: 1000 a 500 ft (300 a 150 m) AGL
Nácvik vzletu, letu po okruhu, rozpočtu a přistání, opravy chybných rozpočtů, přistání s boční, eventuálně zadní složkou větru.
Podmínky splnění: Provést let po okruhu, s přiměřenou přesností dodržet rychlost, výšku letu, tvar okruhu, stanovený režim motoru a přistát správným rozpočtem na určeném místě.
6.14. Cvičení 25. Samostatné lety na režimu visení
výška letu: 1 – 10 ft (0,3 – 3 m) AGL
Samostatně procvičit lety ve visu v rozsahu cv. 22.
Podmínky splnění: hodnocení 1-2.
6.15. Cvičení 26. Samostatné lety po okruhu
výška letu: 1000 a 500 ft (300 a 150 m) AGL
Odpoutání do visení, vzlet, let po okruhu, přistání.
Podmínky splnění: hodnocení 1-2.
6.16. Cvičení 27. Samostatný let do prostoru
výška letu: 500- 1500 ft (150 – 500 m) AGL
Let v rozsahu povolených rychlostí od minimální po maximální, zatáčky o náklonu 15 a 30 stupňů ve vodorovném letu, stoupání i klesání, v přímém směru i v zatáčkách.
Podmínky splnění: hodnocení 1-2.
6.17. Cvičení 28. Přezkoušení / pilotní zkouška
výška letu: do 1500 ft (500 m) AGL
Inspektor nebo instruktor provede v souladu s úvodním ustanovením přezkoušení všech prvků techniky pilotáže v rozsahu pilotní zkoušky.
Podmínky splnění: Stejné, jako u pilotní zkoušky.
HLAVA 7. VÝCVIK PRO KVALIFIKACI INSTRUKTOR
7.1. Úvodní ustanovení:
výcvik instruktora ULH provádí inspektor provozu ULH a dle této osnovy jej lze provést pilotům ULH na základě předložení průkazu způsobilosti a zápisníku letů při splnění požadavků dle odstavce – Požadavky na uchazeče
inspektor, který provedl výcvik, vyplní osobní list a zapíše získanou kvalifikaci do zápisníku letů frekventanta.
7.2. Požadavky na uchazeče
1) Uchazeč musí být držitelem průkazu pilota ULH (absolvent základního nebo přeškolovacího výcviku pilota ULH).
2) V době zařazení do výcviku musí dosáhnout věku minimálně 21 let.
3) Uchazeč musí mít nalétáno nejméně 200 hodin jako pilot ULH.
4) Uchazeč musí ovládat slovem i písmem český jazyk.
5) Uchazeč musí úspěšně absolvovat vstupní přezkoušení.
6) Uchazeč musí mít nepřetržitou pilotní praxi minimálně 5 let.
7.3. Uznání kvalifikace instruktora
Držitelům platných průkazů Soukromý pilot vrtulníků, Obchodní pilot vrtulníků, Dopravní pilot vrtulníků a pilotům vojenských vrtulníků s kvalifikací instruktor může inspektor provozu ULH udělit kvalifikaci instruktora ULH bez absolvování výcviku dle oddílu VÝCVIK INSTRUKTORA, pokud absolvovali přeškolovací výcvik této osnovy s tím, že nejméně 50% letové doby ve dvojím řízení absolvovali při přeškolování z instruktorského sedadla.
7.4. Osnova výcviku instruktora ULH
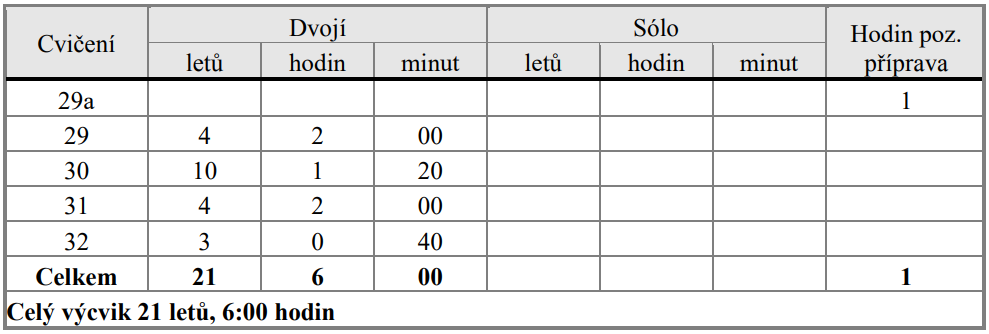
7.5. Cvičení 29a (Pozemní příprava)
Cvičený pilot předvede výuku pozemní přípravy v rozsahu HLAVA 4, ÚLOHA 1, cvičení 22a – 22b této osnovy.
7.6. Cvičení 29. Cvičné lety na režimu visení
výška letu: 1-10 ft (0,3 – 3 m) AGL
Visení na místě, svislé odpoutání a dosednutí, otáčení ve visu na místě, posuny do stran, dopředu a dozadu. Při všech letech řídí adept ULH z instruktorského sedadla. Na sedadle pilota sedí inspektor.
Adept vysvětluje inspektorovi postup provedení jednotlivých prvků, reaguje na případné simulované chyby a vysvětluje jejich odstranění.
Podmínky splnění: Předvedení všech prvků pilotáže v potřebné kvalitě, při simulované chybě žáka schopnost zajistit včasným zásahem bezpečnost letu a vysvětlit jak chybu odstranit.
7.7. Cvičení 30. Cvičné lety po okruhu
výška letu: 1000 a 500 ft (300 a 150 m) AGL
Vzlet, let po okruhu, rozpočet, přistání. Opravy chybných přistání, přistání s boční eventuálně zadní složkou větru. Při všech letech řídí adept ULH z instruktorského sedadla. Na sedadle pilota sedí inspektor.
Adept vysvětluje inspektorovi postup provedení jednotlivých prvků, reaguje na případné simulované chyby a vysvětluje jejich odstranění.
Podmínky splnění: Předvedení všech prvků pilotáže v potřebné kvalitě, při simulované chybě žáka schopnost zajistit včasným zásahem bezpečnost letu a vysvětlit jak chybu odstranit.
7.8. Cvičení 31. Cvičné lety do prostoru
výška letu: do 1500 ft (500 m) AGL
Lety v rozsahu povolených rychlostí od minimální do maximální, zatáčky o náklonu 15 a 30 stupňů v horizontálním letu, stoupání a klesání, řešení zvláštních případů za letu, klesání autorotací v přímém směru i v zatáčkách až do visení. Přistání na plochu omezených rozměrů. Při všech letech řídí adept ULH z instruktorského sedadla. Na sedadle pilota sedí inspektor. Adept vysvětluje inspektorovi postup provedení jednotlivých prvků, reaguje na případné simulované chyby a vysvětluje jejich odstranění.
Podmínky splnění: Předvedení všech prvků pilotáže v potřebné kvalitě, při simulované chybě žáka schopnost zajistit včasným zásahem bezpečnost letu a vysvětlit jak chybu odstranit.
7.9. Cvičení 32. Závěrečné přezkoušení
výška letu: do 1 500 ft (500 m) AGL
Inspektor přezkouší frekventanta v rozsahu pilotní zkoušky a posoudí jeho schopnost k provádění letů ve funkci instruktora. Při letech řídí adept ULH z instruktorského sedadla. Na sedadle pilota sedí inspektor.
Adept vysvětluje inspektorovi postup provedení jednotlivých prvků, reaguje na případné simulované chyby a vysvětluje jejich odstranění.
Podmínky splnění: Předvedení všech prvků pilotáže v potřebné kvalitě, při simulované chybě žáka schopnost zajistit včasným zásahem bezpečnost letu a vysvětlit jak chybu odstranit. Schopnost vykonávat funkci instruktora.
7.10. Zkouška instruktora:
7.10.1. Teoretická část
– Písemný zkušební test (zkušební testy určuje hlavní inspektor provozu ULH).
– Ústní zkouška ze schopnosti vyučovat letecké předměty a vysvětlit prvky pilotáže a možné chyby.
Podmínky splnění: Prokázat teoretické znalosti dosažením předepsaného počtu bodů z testu, prokázat před tříčlennou zkušební komisí jmenovanou hlavním inspektorem provozu ULH schopnost vyučovat letecké předměty a správně popsat a vysvětlit jednotlivé prvky pilotáže s upozorněním na možné chyby a jejich důsledky.
7.10.2. Praktická část
obsahuje min. 2 lety ve dvojím v době trvání 30 min.:
1. let s inspektorem v prostoru, při kterém zkoušející (na sedadle instruktora) ověřuje úroveň techniky pilotáže v rozsahu cvičení předepsaných výcvikovou osnovou včetně popisu provádění jednotlivých prvků pilotem, ověřuje úroveň letu po okruhu včetně popisu provádění jednotlivých fází pilotem.
Do letu inspektor zařadí nácvik nouzového přistání po vysazení motoru.
2. let s inspektorem, kde zkoušející (na pilotním sedadle) ověřuje úroveň přezkušovaného v ovládání letounu z instruktorského sedadla. Po část letu sám řídí a na úmyslně prováděných chybách ověřuje úroveň přezkušovaného v jejich hodnocení a opravách.
Podmínky splnění: Prokázat před inspektorem zvládnutí všech prvků techniky pilotáže požadovaných pro kvalifikaci pilot, avšak s hodnocením 1 až 2, tj. velmi dobré praktické schopnosti. Tyto schopnosti musí prokázat i při pilotáži ze sedadla instruktora. Dále musí prokázat během letu schopnost správně určovat a opravovat chyby pilotáže, simulované inspektorem a jejich závažnost klasifikovat v souladu s hodnotící stupnicí.
HLAVA 8. ÚLEVY PŘI VÝCVIKU
8.1. Teorie
Piloti s kvalifikací pilota vrtulníku ATPL(H), CPL(H), PPL(H) nebo piloti vojenských vrtulníků nemusí absolvovat teoretickou výuku, pouze prostudují předměty PRAVIDLA LÉTÁNÍ, STAVBA A KONSTRUKCE SLZ, předpisy LAA a vykonají z nich zkoušku. Zkoušku provede ústně, nebo formou písemného či počítačového testu inspektor provozu ULH.
Piloti s kvalifikací pilota letounů udělenou ÚCL nebo AČR, piloti ULL a piloti motorových kluzáků nemusí absolvovat teoretickou výuku, pouze prostudují předměty PRAVIDLA LÉTÁNÍ, STAVBA A KONSTRUKCE SLZ, AERODYNAMIKA, předpisy LAA a vykonají z nich zkoušku. Zkoušku provede ústně, nebo formou písemného či počítačového testu inspektor provozu ULH.
8.2. Praxe
Základní výcvik musí být proveden v rozsahu nejméně 34:20 letových hodin absolvovaných v průběhu posledních 24 měsíců před zkouškou..
Pilotům s kvalifikací pilota letounů udělenou ÚCL nebo AČR, pilotům ULL a pilotům motorových kluzáků je možno snížit počet letových hodin na 25.
Piloti s kvalifikací ATPL(H), CPL(H), PPL(H) nebo piloti vojenských vrtulníků absolvují výcvik podle osnovy přeškolovacího výcviku dle Hlavy 6 včetně pilotní zkoušky v rozsahu min. 4 hodin 30 min.
Poznámka: O snížení počtu letových hodin v jednotlivých cvičeních rozhodne instruktor dle schopností žáka.
8.3. Kvalifikace instruktora:
Držitelům platných průkazů Soukromý pilot vrtulníků, Obchodní pilot vrtulníků, Dopravní pilot vrtulníků a pilotům vojenských vrtulníků s kvalifikací instruktor lez udělit kvalifikaci instruktora ULH bez absolvování výcviku dle oddílu VÝCVIK INSTRUKTORA, pokud absolvovali přeškolovací výcvik této osnovy s tím, že nejméně 50% letové doby ve dvojím řízení absolvovali při přeškolování z instruktorského sedadla.
8.4. Kvalifikace zkušebního pilota:
Piloti ATPL(H) a CPL(H) s platnou kvalifikací zkušební lety provozní a nebo zkušební lety bez omezení mohou získat kvalifikaci zkušební pilot na základě provedení příprav(výuky) v rozsahu cv. 39.a, a přezkoušení inspektorem s kvalifikací zkušební pilot dle cv. 43.bez dalších formalit
HLAVA 9. VÝCVIK PRO KVALIFIKACI ŘÍZENÉ LETY VFR
9.1. Požadavky pro zařazení do výcviku:
Do výcviku může být zařazen uchazeč s platným průkazem ULH a nejméně omezeným průkazem radiofonisty, nebo vyšším. Výcvik provádí instruktor s kvalifikací řízené lety VFR. Absolvování výcviku potvrzuje do osobního listu uchazeče. Přezkušovací let provádí inspektor ULH s kvalifikací řízené lety VFR a výsledek zapíše do osobního listu uchazeče.
Získanou kvalifikaci vpisuje do průkazu ústřední rejstřík LAA na základě osobního listu.
9.2. Pilotům s platným průkazem ATPL (A či H), CPL (A či H), PPL(A či H), TMG s kvalifikací ŘL VFR a jakéhokoli jiného průkazu pilota SLZ s kvalifikací ŘL VFR může být kvalifikace ŘL VFR zapsána do průkazu pilota ULH bez dalších formalit.
9.3. Výcviková osnova:
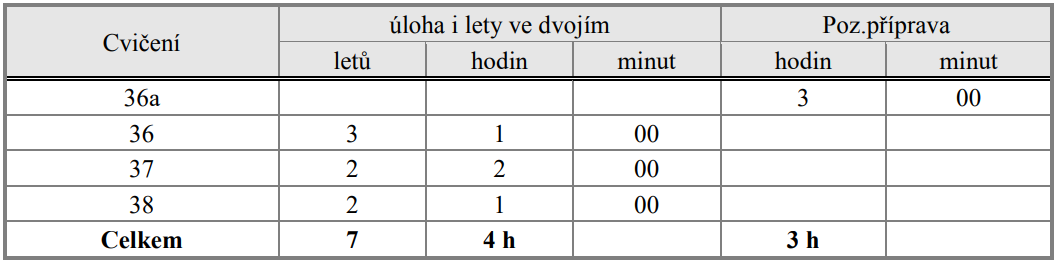
9.4. Cvičení 36a (Pozemní příprava)
Teoretická příprava v rozsahu 3 hodin musí obsahovat zásady letů v řízeném prostoru, podání letového plánu, práce s AIP, NOTAM a mapami, vstupní a výstupní body, standardní tratě, schopnost pilota získávat informace pro let v řízeném prostoru postupy pro nastavení výškoměru a vyjadřování výšky, nácvik radiokorespondence, zásady použití odpovídače sekundárního radaru.
9.5. Cvičení 36. Kontrolní navigační let s přistáním na letištích AFIS:
výška letu: 500 – 1000 ft (150 – 300 m) AGL
Provést kontrolní navigační let s mezipřistáním na dvou letištích AFIS.Ověřit schopnost vést ULH po stanovené trati a ve stanovené výšce a provést přistání a vzlet na letišti AFIS se správnou
radiokorespondencí.
Podmínka splnění: Vedení vrtulníku po stanovené trase s přiměřenou přesností, vedení navigačního záznamu. Správný postup příletu na letiště AFIS včetně radiokorespondence přistání, vzletu a odletu.
9.6. Cvičení 37. Navigační let s přistáním na řízeném letišti:
výška letu: 500 – 1000 ft (150 – 300 m) AGL
Provést navigační let s úplným přistáním na řízeném letišti. Pilot vyplní pro daný let letový plán a vede radiokorespondenci.
Podmínka splnění: Vedení vrtulníku po stanovené trase s přiměřenou přesností, vedení navigačního záznamu. Správný postup příletu na řízené letiště včetně přistání, vzletu a odletu.
9.7. Cvičení 38. Přezkušovací navigační let s přistáním na řízeném letišti
výška letu: 500 – 1000 ft (150 – 300 m) AGL
Přezkoušecí navigační let s úplným přistáním na řízeném letišti. Přezkoušení provádí inspektor s kvalifikací ŘL VFR.
Podmínka splnění: Vedení vrtulníku po stanovené trase s přiměřenou přesností, vedení navigačního záznamu. Správný postup příletu na řízené letiště včetně přistání, vzletu a odletu.
HLAVA 10. VÝCVIK PRO KVALIFIKACI ZKUŠEBNÍ PILOT
10.1. Požadavky pro zařazení do výcviku:
Do výcviku může být zařazen uchazeč s platným průkazem ULH a celkovým náletem nejméně 200 hodin, z toho nejméně 100 hodin na ULH. Výcvik probíhá zpravidla formou kurzu vedeného inspektorem s kvalifikací zkušební pilot, jehož k tomuto účelu pověří hlavní inspektor ULH. Lety eviduje inspektor v Osobním listu uchazeče.
10.2. Úlevy při výcviku
Piloti ATPL(H) a CPL(H) s platnou kvalifikací zkušební lety provozní a nebo zkušební lety bez omezení mohou získat kvalifikaci zkušební pilot na základě provedení příprav(výuky) v rozsahu cv. 39.a, a přezkoušení inspektorem s kvalifikací zkušební pilot dle cv. 43.bez dalších formalit. Na základě vyplněného osobního listu provede ústřední rejstřík LAA vepsání kvalifikace do průkazu.
10.3. Výcviková osnova zkušebního pilota:
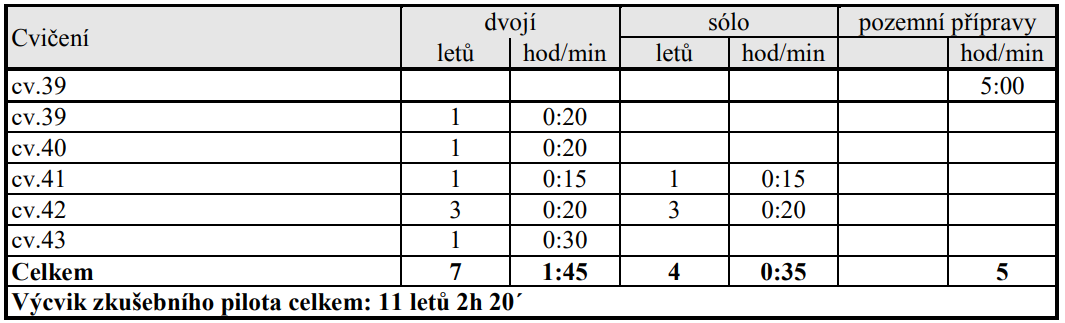
10.4. Cvičení 39a (Pozemní příprava – teoretická výuka)
Teoretická příprava v rozsahu 5 hodin musí obsahovat zásady prohlídky, technické kontroly ULH před letem a kontrolu funkčnosti na zemi, zjištění těžiště vážením a výpočtem, zásady vyvažování nosného rotoru, ocasní vrtulky a případně chladícího ventilátoru na zemi a za letu, posloupnost zkušebních letů, záletový protokol a letovou příručku.
10.5. Cvičení 39. Let za účelem vyvažování rotoru, ocasní vrtulky a případně chladícího ventilátoru.
Výška letu do 1000 ft (300 m) AGL
Provést nácvik letu za účelem zjištění úrovně vibrací nosného rotoru, ocasní vrtulky a případně chladícího ventilátoru pomocí akcelerometru se stroboskopickou lampou pro účely dynamického vyvažování na zemi, ve visu a při stanovených režimech za letu.
Podmínka splnění: Prokázat schopnost provádět za pomoci vyškoleného technika měření úrovně vibrací a dynamické vyvažování nosného rotoru, ocasní vrtulky a případně chladícího ventilátoru.
10.6. Cvičení 40. Let za účelem kontroly vybavení
Výška letu do 1000 ft (300 m) AGL
Provést nácvik motorové zkoušky, zkoušky volnoběžné spojky, řízení a kontroly vybavení, přístrojů, instalací na zemi i za letu.
Podmínky splnění: Prokázat schopnost provádět kontrolu veškerého zařízení na zemi i za letu.
10.7. Cvičení 41 Let pro ověření výkonů a vlastností
Výška letu do 1000 ft (300 m) AGL
Provést nácvik letu pro ověření vlastností v celém rozsahu rychlostí a režimů od visu až po Vne, ve vírovém prstenci a při vypočtených minimálních otáčkách rotoru, ověření stability, posouzení vlastností včetně vyvažitelnosti a tíživosti a zjištění výkonů. Jeden let provést při minimální možné hmotnosti a druhý při maximální hmotnosti.
Podmínky splnění: Prokázat schopnost provádět lety pro ověření výkonů a vlastností.
10.8. Cvičení 42 Let pro ověření vlastností v autorotaci, nácvik nouzových přistání
Výška letu do 1000 ft (300 m) AGL
Provést nácvik letu pro ověření vlastností při klesání v autorotaci, zjištění parametrů pro základní nastavení listů rotoru a nácvik nouzového přistání.
Podmínky splnění: Prokázat schopnost provádět autorotace a zjišťovat potřebné parametry pro základní nastavení listů nosného rotoru.
10.9. Cvičení 43 Závěrečné přezkoušení
Výška letu do 1000 ft (300 m) AGL
Provést přezkušovací let k ověření schopnosti uchazeče samostatně seřizovat a zalétávat ULH.
Podmínky splnění: Prokázat schopnost seřizovat a zalétávat ULH.
HLAVA 11. PŘÍLOHY
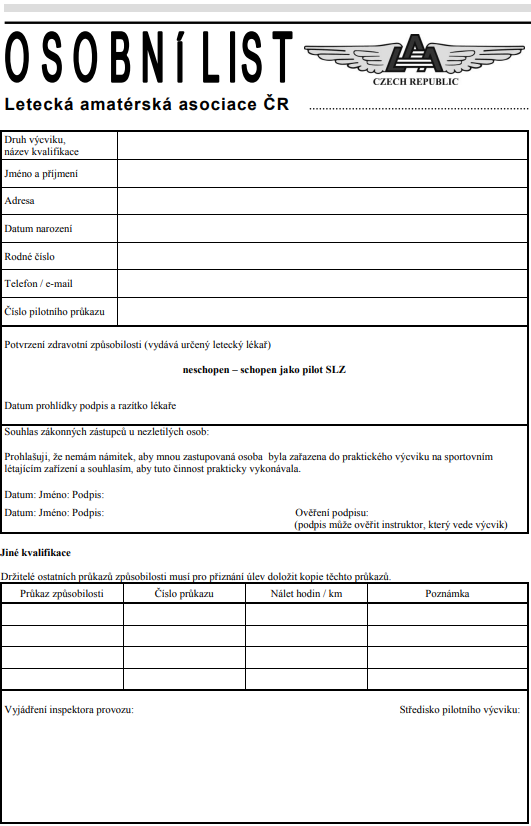
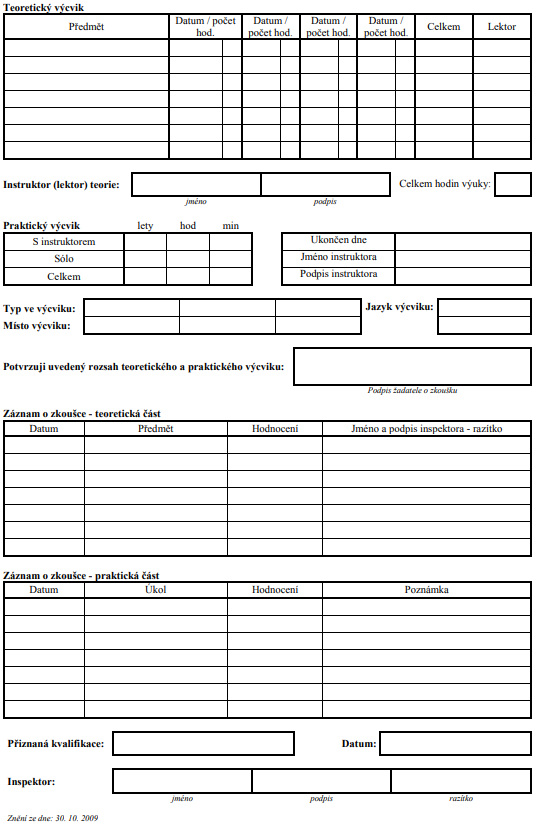
11.1. Osobní list